Mortgage 101
Learn about mortgage terminologies and mortgage types.
Mortgage terms you need to know
6 min
- What mortgage terms you’ll see while purchasing a home
- What common mortgage jargon actually means
- How to confidently communicate and navigate through your home buying journey

Amortization period. Loan to value. Prime rate. When researching mortgages online, it can feel like learning a new language. So, what terms do you need to know?
A mortgage is typically one of the largest financial commitments of your life, so you want to make sure you understand all the details. Around homeownership, jargon can run wild. The frequent use of uncommon words around purchasing a home can create a learning curve. Let’s dive into this vocabulary so you’ll be speaking fluent mortgage in no time.
This glossary of mortgage terms can help you navigate the home-buying journey and confidently discuss the financial steps along the way.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Amortization Period | An amortization period is the time it takes to pay off your mortgage in full. What you need to know is a shorter amortization period makes your mortgage payments larger and you will pay off your mortgage faster. A longer amortization period makes your mortgage payments smaller, but it'll take longer to pay off your mortgage. |
| Annual percentage rate (APR) |
When it comes to your mortgage, annual percentage rate (APR) is the yearly cost of borrowing, including all interest and non-interest charges. It is used as a standardized way to decide between the rates of different lenders, and before an agreement is finalized, they are required to share the APR of the loan with you. For example, let’s say you’re considering this mortgage loan:
But when purchasing the house you have other expenses. Let’s say for this loan you have an appraisal fee of $300. This amount, lumped in with your loan amount, creates your APR and the corresponding weekly payment. In this case it would be:
*for illustrative purposes only It’s important to note that APR doesn’t include compounding interest and lenders may exclude certain fees from their APR calculation. You can ask for more information about what fees a lender does or doesn’t include in your communications with them. |
| Creditor insurance |
Creditor insurance covers mortgage debt you may have, in case of critical illness, death, and disability. It can allow you to feel confident, knowing that if something unexpected were to happen, you and your family would be able to stay in your home. Creditor insurance can include: mortgage life insurance, mortgage critical illness insurance, mortgage disability insurance, or other insurance options depending on the provider. These insurance types are optional, but having them offers valuable peace of mind. |
| Default insurance |
Mortgage default insurance protects lenders if a borrower is unable to repay their mortgage and is a regulatory requirement of the Canadian government for high ratio mortgages (less than 20% down payment). Default insurance can be paid in a lump sum at the time of getting your mortgage or it can be added to your mortgage and included in your payments. |
| Down payment |
A down payment is a sum of money you pay upfront for a home. It’s typically represented as a percentage of the total cost of your home. Conventional wisdom recommends putting down 20% of the overall cost of the home as a down payment. Doing this offers benefits, like eliminating the need to buy mortgage default insurance. |
| Fixed-rate mortgages |
Fixed-rate mortgages lock in your interest rate and protect you from rate increases for a set term. Since your rate stays the same throughout your mortgage term, you’ll always know the exact amount your payments will be during that term. They are the most popular mortgage type because their stability makes it easy to plan ahead and budget. |
| High-ratio mortgage |
A high-ratio mortgage is any mortgage where the down payment is less than 20% on a home purchase of less than a million dollars. It is called a “high-ratio” because the ratio between the loan and the value of the property (called LTV or loan-to-value) is high. Any loan-to-value ratio where the mortgage loan is greater than 80, to a maximum 95%, is considered a high-ratio mortgage. For example: Property value: $500,000 Down payment: $70,000 (14% of the property value) Mortgage amount: $430,000 Since the down payment is less than 20% of the property value or the LTV ratio is 86%, the mortgage amount is considered a high-ratio mortgage. When you get a high-ratio mortgage, it will require you to have mortgage default insurance On the other hand, any mortgage where the down payment is more than 20% or the LTV or less than 80% is referred to as a “low-ratio mortgage”. Low ratio mortgages do not need a mortgage default insurance. |
| Loan-to-value (LTV) |
Loan-to-value (LTV) is the ratio of your loan amount to the value of the home you’re purchasing. Lenders often use LTV to determine the risk-level of a mortgage loan. A LTV of more than 80% is generally considered to be a high-risk loan. |
| Mortgage Term |
A mortgage term is the length of time you are committing to your mortgage agreement for a set interest rate. Mortgage terms usually vary from 1 to 5-years, but you may also sometimes find 10-year terms available. For example, if you have a 5 year fixed-rate mortgage at 2% you’re agreeing to pay 2% interest on your mortgage amount for 5 years. At the 5 year mark you can continue another 5 years or change to a new length that suits you better. At this time your mortgage rate can change (depending on the current market offering) and you have the opportunity to switch lenders if you like. |
| Prequalification (Affordability calculator) |
A prequalification (using an affordability calculator
) lets you estimate the maximum mortgage amount you can afford based on your reported income and expense. Typically, you start this process if you’re considering getting into homeownership and want to plan and budget for a future purchase.
|
| Prime rate |
The prime rate is used by banks and financial institutions to price their variable-rate mortgages. Every lender’s prime rate is slightly different but they can be affected by changes to the Bank of Canada (BoC) policy rate—the interest rate that major financial institutions are subject to while borrowing and lending funds. The BoC policy rate changes based on the current economic climate. When the economy is strong, the BoC may raise its policy rate to help curb inflation. And similarly, when the economy is weak, the BoC may lower the policy rate to stimulate economic growth to protect from deflation. However, lenders may choose not to adjust their prime rate even if the policy rate changes. |
| Refinance | Refinance is borrowing more money through your mortgage by leveraging the equity in your home. This can be a useful way to access funds for expenses (like repairs or renovations) or consolidating debt. |
| Renewal | Renewal (sometimes also called renewing) refers to when your current mortgage term ends, and you have the choice to renegotiate your mortgage terms with your current lender or you switch to a new lender to negotiate a better rate or terms. |
| Stress test |
The mortgage stress test requires financial institutions to make sure a borrower can still make mortgage payments if the Bank of Canada's (BoC) prime interest rate increases. When applying for a new mortgage, switching lenders, or borrowing additional money against your home’s equity, you must qualify for whatever is higher: the given interest rate plus 2%, or the Mortgage Qualifying Rate (MQR) set by the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI). The stress test was first introduced in 2017 to make sure new home purchasers weren't borrowing more than they could afford and ensuring they could manage payments if there was a sudden rise in interest rates. |
| Variable-rate mortgage |
The act of an option writer who will be delivering (in the case of a call) shares of an underlying stock to a customer or buying (in the case of a put) shares of an underlying stock from a customer when the option contract is exercised. A variable-rate mortgage is attractive if rates decline, which may help you save over the term of your mortgage. However, if the prime rate increases, so will your rate and payments. |
House hunting with confidence
While you’re searching for your perfect home, this glossary can help you navigate the financial aspects of making it yours. But, there are more ways you can make the process easier.
If you’re in the early stages of considering getting into homeownership, you can start with understanding an estimate of how large of a mortgage you can afford. You can do this by using an affordability calculator which also helps you estimate your potential month payments. This is a helpful step so you can plan and budget for a future home purchase.
Go house hunting with confidence. Get my rate now.
Learn more about QuestMortgage.
The information in this blog is for informational purposes only and should not be used or construed as real-estate, mortgage, financial or investment advice.
Fixed vs variable mortgage: what's the difference?
5 min
- The difference between a fixed and variable rate mortgage
- When a fixed-rate mortgage may be the right option for you
- When a variable-rate mortgage may be the right option for you

For most Canadians, you don’t hear a lot about interest rates until you’re buying a home or your mortgage is up for renewal. Then, suddenly it’s all you can think about. Fixed rates are rising? But variable rates are staying the same? How does it all work?
That’s why we’re here. Mortgage rates are expected to remain low until the economy has fully recovered. Considering we’re in a low-rate environment, you may think that it makes sense to lock in a fixed-rate mortgage. But is a fixed-rate mortgage the best option that will save you the most money? Let’s dive into the fixed vs variable mortgage debate to answer that question. We’ll look at the key differences so that you can make an informed decision when it comes to your mortgage and you can keep more of your money.
Fixed vs variable mortgage – what’s the difference?
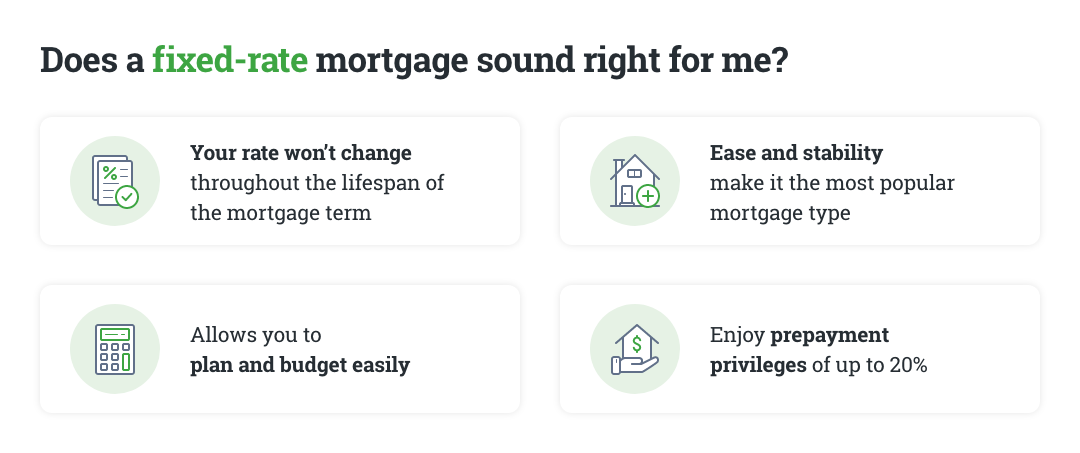
While fixed and variable rate mortgages are opposites, one isn’t better than the other. With fixed-rate mortgages, you can take comfort knowing your mortgage payments and interest rate will always be the same. Choosing a fixed-rate mortgage also allows you to lock in your interest rate and protects from rate increases. Since your rate stays the same throughout your mortgage term, you’ll always know exactly what your payments will be.
With variable-rate mortgages, your payments and interest rate will fluctuate based on the prime rate, which we’ll discuss in a minute. A variable-rate mortgage is attractive if rates decline, which may help you save over the term of your mortgage. However, if the prime rate increases, so will your rate and payments. Both types of mortgages have their positives. So, it really just depends on your personal situation and what you feel most comfortable with.
How are mortgage rates set?
The Bank of Canada (BoC) sets its policy rate, which is the interest rate that major financial institutions borrow and lend funds at based on the current economic climate.
When the economy is strong, the BoC may raise its policy rate to keep up with inflation. And similarly, when the economy is weak, the BoC may lower the policy rate to stimulate economic growth and keep inflation from falling. Changes to this policy influence the prime rate which is used by banks and financial institutions as a basis for pricing variable rate mortgages. However, if the policy rate changes, the banks may or may not choose to adjust their prime rate.
Fixed rates are determined differently and are generally tied to the Canadian Bond market. As bond yields (the rate of return a bond provides) rise, so will fixed mortgage rates. However, once your fixed-rate mortgage is locked for your mortgage term, your own mortgage rate won’t change until it’s time for you to renew.
When does a fixed-rate mortgage make sense for you?
For many Canadians, a fixed-rate mortgage is a great option. When you can secure a great, low rate, it makes perfect sense to want to lock it in. With a fixed-rate mortgage, it’s something you don’t need to think about, regardless of if rates rise or fall. So, if you’re looking for ease and stability, a fixed-rate option may make the most sense for you. Stability also makes it easier to plan and budget, since you’ll know exactly what your payments will be.
When does a variable-rate mortgage make sense for you?
A variable-rate mortgage is another great option and can help you save more in low-rate environments. Variable-rate mortgages will typically start at a lower rate (than a fixed rate mortgage), so there’s a bit more flexibility and room if rates start to rise. Also, the prepayment penalty may be lower with a variable-rate mortgage, which is key if you’re unsure about committing to the term of your mortgage.
There is also the option to switch a variable-rate mortgage to a fixed-rate mortgage to lock in your rate. Check out our rates page to see our great, low rates.
So, which option should you choose?
There is no one-size-fits all answer – it’s whatever works for you. Both mortgage options can help you save money and get you into the housing market, which is the main goal.
If you're looking for a mortgage or think you're going to be soon, check out QuestMortgage for great, low rates and the best prepayment privileges that can help you pay off your mortgage sooner. You have the option of making additional lump sum payments up to 20% of the original balance at the start of the term. Plus, you can increase your mortgage payments at any time (up to 100%), so you can pay off your mortgage sooner.
If the overnight rate is something that keeps you up at night and you’d prefer to have your payments stay the same, then a fixed-rate mortgage may be the better option for you. But if you’re in a low-rate environment and feel comfortable with the unknown if it means saving over the long term, then the variable rate option may be best for you.

If you’re in the market for a mortgage, check out our mortgage affordability calculator to see how much you can afford.
Learn more about QuestMortgage.
The information in this blog is for information purposes only and should not be used or construed as financial or investment advice by any individual. Information obtained from third parties is believed to be reliable, but no representations or warranty, expressed or implied is made by Questrade Group of Companies or any other person to its accuracy.
The prime rate in Canada: What you need to know
7 minutes

What you’ll learn:
- What the prime rate is
- How the prime rate is set
- How the prime rate influences mortgage rates
Between prime rates, policy interest rates, and overnight rates, it can seem like being a first-time home buyer is all about decoding confusing lingo. Let’s break down the different types of rates so you can navigate the housing market with confidence.
What is the prime rate?
Let’s start by breaking down the burning question—what is the prime rate exactly?
To put it simply, the prime lending rate is the interest rate that the major banks and financial institutions in Canada use to determine interest rates for loans with variable interest rates. For example, the prime rate influences interest rates for variable-rate mortgages and home equity lines of credit.
Individual banks and financial institutions have their own prime rates, which are based off of the BoC’s policy interest rate. We'll discuss more about the policy interest rate below.
How is the prime rate determined?
The prime lending rate is influenced by the BoC's policy interest rate (also known as overnight rate)—the interest rate that banks charge each other to borrow and lend from one another in the overnight market.
When the BoC increases its policy interest rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money. To cover this additional cost, banks raise their prime rates to receive more interest from consumers. Generally, when the BoC decreases the overnight rate, banks lower their prime rates as well, but there are exceptions.
Although each bank determines its own prime rate, the big six Canadian banks tend to have similar prime rates. When the BoC’s overnight lending rate changes, so will the the prime rates of these banks.
Why does the prime rate change?
To answer this, we should first understand why the BoC exists. The BoC’s primary goal is to “promote the economic and financial welfare of Canada”. It raises its policy interest rate to manage inflation or lowers it to stimulate the economy.
Changes to the policy interest rate may influence the prime rates, which banks and financial institutions use to price variable rate loans. However, banks may or may not choose to adjust their prime rate.
How does the prime rate impact mortgage rates?
Before we get into how the prime rate affects mortgage rates, it’s important to note that, in Canada, there are two main types of mortgage rates: variable and fixed. The prime rate affects both types differently.
When you get a variable-rate mortgage, your regular payments may change depending on the prime rate in Canada. Although the variable rate you receive at the start of your mortgage term is typically lower than the fixed rate you would receive for a similar term, your variable-rate could increase or decrease throughout your mortgage term—depending on how the prime rate changes. If you choose a variable-rate mortgage and the prime rate plunges, you could potentially save money on interest. However, if the prime rate rises, your regular mortgage payments may increase.
On the other hand, getting a fixed-rate mortgage means you will pay the same rate over the duration of your mortgage term. Your regular payments will not change, regardless of any changes in the housing market or the prime rate.
However, even though the prime rate doesn’t affect your fixed rate during your mortgage term, it indirectly impacts the fixed rate you receive at the beginning of your mortgage term, or when your mortgage comes up for renewal. As a new borrower or homeowner, the fixed rate you get at the start of your mortgage term is based on how the prime rate is expected to change in the future. That said, there are also other factors that determine how the fixed rate is set.
How often does the prime rate change?
Prime rate changes usually coincide with rate announcements by the Bank of Canada. The BoC typically has eight policy rate announcements a year, and they are scheduled well in advance. The next rate announcement is scheduled to take place on September 7, 2022.
The remaining dates for policy interest rate announcements in 2022 are:
- Wednesday, October 26
- Wednesday, December 7
The BoC has also published its 2023 schedule for the release of its policy interest rate decisions.
Now that you understand what the prime rate is and how it influences mortgage rates, let’s talk about the next steps for you in your homeownership journey.
See how much you could afford
The search for the perfect home for you can be especially exciting. But before you begin house-hunting, you’ll want to understand how much mortgage you could afford. Our Affordability Calculator offers you an estimate of what size mortgage you could afford and a look at what your monthly mortgage payments could be.
Get pre-approved with QuestMortgage
If you’re in the market for a mortgage and planning to purchase a home within the next four months, consider getting pre-approved with QuestMortgage. A mortgage pre-approval is a great way to determine how much mortgage you can afford, and the interest rate you could get approved for.
You can lock in a great, low rate with QuestMortgage for 120 days, which can help you house hunt with confidence.
GET MY PRE-APPROVAL RATEIf you enjoyed this post, please consider sharing it on Facebook or Twitter.
P.S. We’d love to meet you on Twitter here or on Facebook here.
The information in this blog is for information purposes only and should not be used or construed as financial or investment advice. Information obtained from third parties is believed to be reliable, but no representations or warranty, expressed or implied, is made by Questrade Group of Companies, its affiliates or any other person to its accuracy.
Factors that could impact your mortgage rate
8 minutes

When considering your mortgage, you’ll encounter a variety of rates and it may seem like they’re changing almost weekly. That’s because they most likely are. Let’s explore the science behind mortgage rates, so you can stay informed on your options and secure the best rate for you.
If you’re in the market for a mortgage, you’ve probably already noticed that rates are in constant flux. Besides shopping around for the lowest rate, there are a few things you can do to set yourself up to succeed in today’s mortgage world. First, you’ll want to learn about the various factors that impact your rate. This will give you a better idea of what range you should expect and help you confidently find or negotiate the right rate for you. Let’s run through seven of these factors below:
- Your mortgage type
- Your down payment amount
- Inflation
- Economic conditions
- Your credit score
- Your mortgage term
- Prepayment risk
The type of mortgage you select will influence the mortgage rate you receive. Let’s get into the difference between the two mortgage types and delve into what they could mean for you, so you can decide which one best fits your needs.
With a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly payments remain the same over the course of your mortgage term. Fixed-rate mortgage rates are primarily influenced by Canadian bond yields. These are the returns that you get on a bond (including interest, coupon, or payments) during its term length. Before you start tracking 5-year bond yields though, it’s better to view them as a helpful tip-off of the general direction of fixed rates rather than a precise predictor.
Alternatively, if you choose a variable-rate mortgage, your payments may increase or decrease from month to month, according to your lender’s prime rate. Many mortgage providers use the Bank of Canada’s (BoC) target overnight lending rate (or policy interest rate) to determine their prime rates. The overnight lending rate is the rate that banks charge each other to borrow and lend funds daily. The BoC raises, holds, or drops its overnight lending rate every six weeks, so that banks can follow suit and adjust their prime rates similarly. Ultimately, changes in the policy interest rate directly affect rates for variable-rate mortgages and they can also indirectly impact long-term mortgage interest rates.
Note, variable rates may start out above or below the comparable fixed rate. This depends on the factors mentioned above and how lenders predict the overnight lending rate will change in the future.
Mortgages are categorized in two ways: insured or uninsured. Insured rates apply when your property value is less than one million, your amortization is within 25 years, and your down payment is less than 20% of the purchase price. Also, the minimum down payment for an insured mortgage is 5% on the first $500,000 of the property balance, and 10% on the subsequent value up to $999,999.
For an insured mortgage (also known as a high ratio mortgage), you’ll need to pay mortgage default insurance on top of your mortgage balance. Since the added insurance protects your lender in case you were to default on the loan, lenders often offer lower rates on these mortgages.
Lastly, to qualify for an uninsured mortgage, you’ll need a minimum down payment of 20% of the home’s purchase price. An uninsured mortgage applies when your property value is over one million or the amortization period is greater than 25 years. Since these mortgages don’t require insurance (which protects your lender in case you were to default), uninsured mortgages often come with higher interest rates than insured mortgages.
Inflation—the rate of increase in the prices of goods and services—could also impact the rates that mortgage lenders are willing to offer you. This is because the inflation rate interacts closely with the Bank of Canada (BoC) policy interest rate (also known as its overnight lending rate), which influences the rates that mortgage providers offer borrowers. When inflation rises, the BoC may raise its policy interest rate to lower consumer borrowing power and encourage consumers to borrow and spend less. In this case, lenders may raise their rates too to help compensate for the increased cost of funding mortgages. Similarly, if the BoC lowers its rates due to inflation, lenders usually reduce their rates too.
Aside from inflation, a country’s general economic state can also influence its mortgage rates. To get an idea of how this works, it’s important to first understand that many mortgage providers borrow money from investors and depositors to cover funding for the mortgages they lend to customers. Economic conditions may impact the supply and demand of mortgage funds, which often leads to changes in rates.
Mortgage rates in Canada can also fluctuate based on shifts in foreign markets and economies. This is because Canadian providers may borrow from international investors, like the United States, to help fund mortgages.
Of all the factors that impact your mortgage interest rate, your credit score is one that you get to have a say in. Mortgage lenders use your credit score and report to assess the risk in loaning you money and to determine how likely you are to repay the debt. Essentially, a high credit score shows that you’ve consistently repaid your debts on time in the past. This gives lenders more assurance that you’ll repay the credit they lend you.
With a high credit score, you could access lower mortgage rates and pay less interest, saving you more money on your mortgage over time. So, it’s important to practice healthy credit habits whenever possible. Check out A guide to your credit score and report for a breakdown of the factors that influence your credit and tips on how to build or maintain a good credit score.
A mortgage term refers to how long your mortgage contract is in effect, and it can be as short as six months (although terms that last a few years are more common). After your mortgage term ends, you’ll need to renew your mortgage. So, choosing shorter mortgage terms requires you to renegotiate more often and increases your risk of getting a different interest rate. Ultimately, if you’re looking for stable, consistent mortgage payments and a steady rate, a longer mortgage term with a fixed rate may give you more peace of mind.
Whether you choose an “open” or “closed” mortgage will also impact your overall rate. Often, your lender will offer you a higher interest rate on an “open” mortgage, which you can pay off early without a penalty. If you choose a “closed” mortgage, however, your lender may charge you a significant fee for making lump sum payments beyond allowable limits or paying your mortgage off early. Still, “closed” mortgages often come with a lower interest rate.
What do changing mortgage rates mean for getting a mortgage?
When it comes to your mortgage, understanding how and why interest rates change can help you make better financial decisions. Whether you’re looking to get a mortgage, or renew or switch your current one, let’s see what changing interest rates could mean for you.
Whenever interest rates rise, borrowing money costs more. So, higher mortgage interest rates could increase the amount of money needed to purchase the same home. On the flip side, lower interest rates could help you afford a larger mortgage. In an ever-changing rate environment, it’s always important to consider all your options before committing to a mortgage (or renewing or switching). By doing your homework on your choice of lenders, you can ensure you’re not losing out on potential savings. A mortgage provider with even a slightly lower interest rate could save you up to thousands of dollars on your mortgage.
Discover how much you could save with QuestMortgage ®
At QuestMortgage, we’re committed to getting you a great, low rate right from the start. Selecting a mortgage from our line of BetterRate ® mortgages could help you save on interest and have more money to invest in what matters most to you in life. See what your rate could be in less than one minute.
GET MY RATEThe information in this blog is for information purposes only and should not be used or construed as financial or investment advice by any individual. Information obtained from third parties is believed to be reliable, but no representations or warranty, expressed or implied is made by Questrade Group of Companies or any other person to its accuracy.
Ready to get started?
In just a few clicks see our current rates, then apply for a mortgage in minutes!
Related Lessons
Want to dive deeper?
Preparing for mortgage financing
Learn how to successfully prepare your mortgage application.
View lessonExplore
Mortgage affordability and down payment
Understand how much you can afford and your down payment options.
View lessonThe information in this blog is for information purposes only and should not be used or construed as financial or investment advice. Information obtained from third parties is believed to be reliable, but no representations or warranty, expressed or implied, is made by Questrade Group of Companies, its affiliates or any other person to its accuracy.
All mortgage applications are subject to meeting QuestMortgage standard credit criteria, residential mortgage standards and maximum permitted loan amounts. All rates are subject to change at any time without notice. Advertised interest rates are for approved QuestMortgage applications that meet qualification conditions and interest rates available at pre-approval may be higher. Available in select markets only.
Pre-approval Pre-approval may only be available for certain mortgage terms. The purpose of the pre-approval is to hold an interest rate (for fixed rate mortgage pre-approvals) or to hold a modifier to the QuestMortgage Prime Rate (for variable rate mortgage pre-approvals) for you for the period the Pre-approval Rate Hold Guarantee is in effect and can only be relied upon if you are approved for a QuestMortgage. The Pre-approval Rate Hold Guarantee is in effect from the time you are pre-approved for a period of up to 120 days, after which this guarantee expires; other conditions may apply. Pre-approval does not provide any form of guarantee that you will be approved for a mortgage. The values and figures shown to you cannot be used as an offer to obtain a mortgage or for the approval of any particular mortgage terms. Your approval for a mortgage or a loan requires additional information and verification, and depends on your circumstances at that time. Therefore, you will still be required to go through the full QuestMortgage application process before you may be approved for a mortgage of any kind.